AS/NZS 2885.2 (2016) Revisions
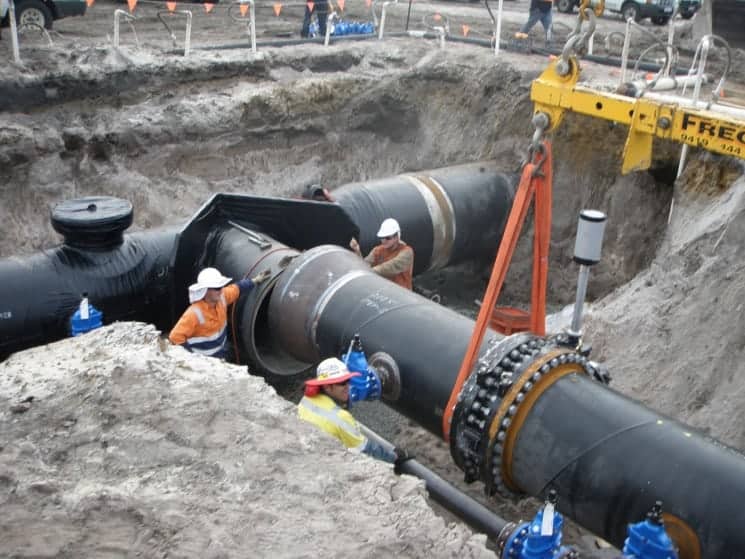
AS 2885.2 (2007) has recently been revised and released as AS/NZS 2885.2 (2016) with a number of improvements and changes. The new revision aims to address previous issues and update the standard in accordance with the current state of pipeline welding.
Section 3 has newly been introduced describing the key tasks involved in pipeline welding and the qualifications required. Of note, a number of tasks are now specifically required to be carried out by an international welding engineer (IWE), such as approval of WPS/PQRs, approval for re-repairs, approval of alternative welding standards (for shop welding of pipeline components), and tasks related to hot-tap in-service welding.
Section 4 includes requirements for materials and consumable and has been revised to cover AS/NZS, AWS, and ISO based consumable classifications. This section now requires that all welding consumables be chemically assessed for boron content (restricted to 0.0010%). This will be important to remember when purchasing consumables and may require that additional batch testing be carried out.
Section 5 has been revised to include additional requirements and further recommendations with regards to the design of a welded joint. Notable additions include the adoption of AS 4041 for forged branch fitting weld requirements and the inclusion of minimum distance between branch / attachment welds and circumferential welds, which shall be at least 1.5 times the pipe diameter.
Section 6 of this revision has also made some noticeable changes to the essential variables for welding procedures. Of particular note is that there is now clear differentiation between requirements for ‘traditional’ cellulosic MMAW (high hydrogen) and the other welding processes (low hydrogen). For example, restrictions with regards to time delay between passes and any change in consumable manufacturer are now clearly only applicable to cellulosic MMAW. Similarly, the maximum wall thickness and maximum carbon equivalent permitted for low hydrogen processes has been relaxed.
Section 7 has had some revisions with regards to Charpy-Vee Notch (CVN) testing which has changed from weld metal only to weld metal and heat-affected zone (HAZ). CVN testing is now required for most butt welds and repair welds and for all defect acceptance criteria levels (i.e. Tier 1, 2, 3).
Appendix C has replaced the previous Appendix E ‘Avoidance of Hydrogen Assisted Cold Cracking (HACC)’. Apart from the change in title there has been no notable change to this section.
Visit LinkedIn for full review comments: www.linkedin.com/company/the-weldnet-pty-ltd
As Australia’s largest group of Welding Engineers, the WeldNet can provide the above services
(info@weldnet.com.au or see www.weldnet.com.au/contact for individual contact details).